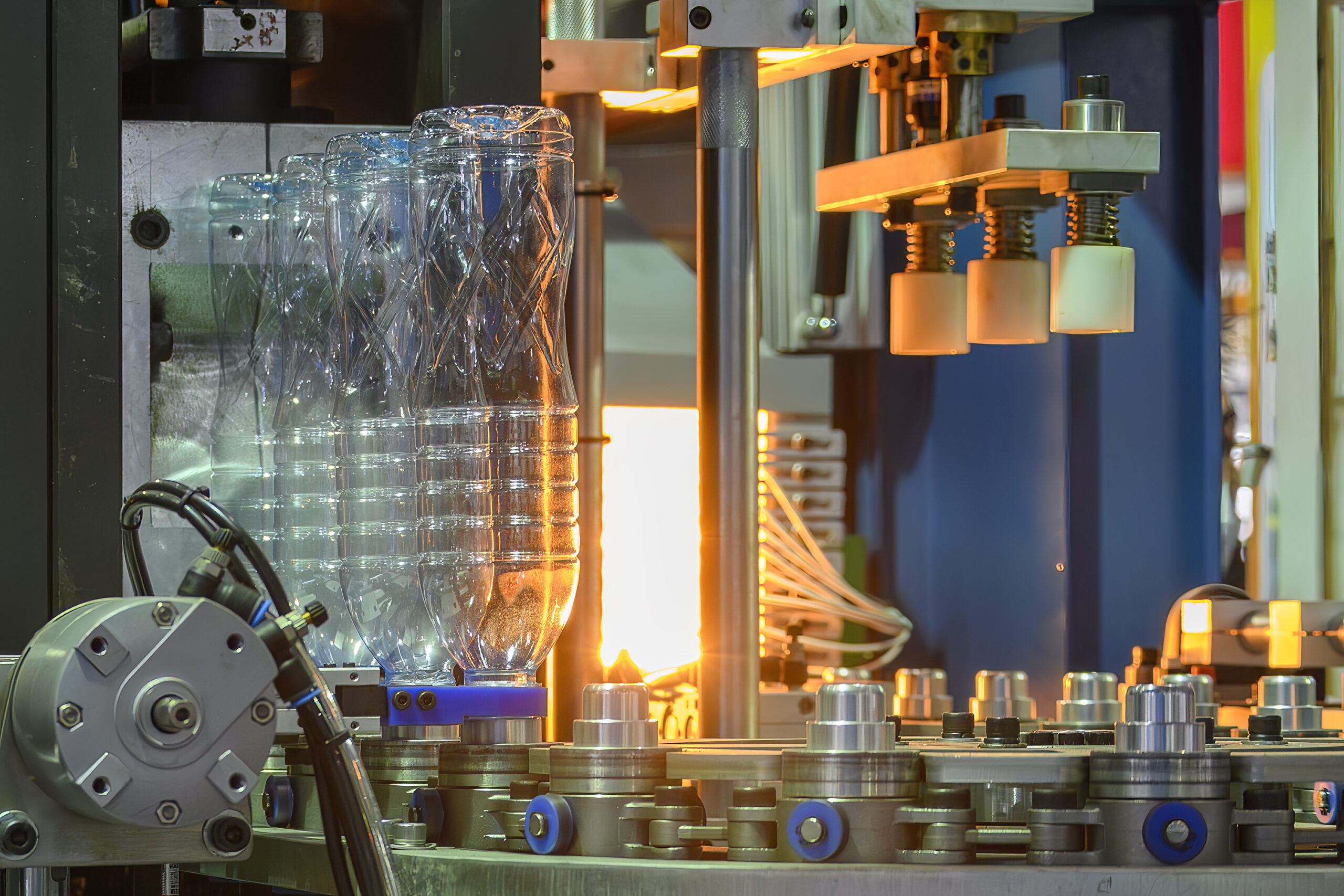
Plastic as a manufacturing material has been around for decades, so one might assume that the industry lacks ongoing innovation. But nothing could be further from the truth. Innovation continues, and an increasing recognition of many specialized resins has led some manufacturers to a noteworthy transition: discontinuing metal part production altogether. Instead, those companies have redesigned those components in plastic.
Misconceptions persist about plastic as a cheap or weak material — myths that give some companies pause when considering such a switch. However, in the match-up between plastic vs. metal, there are scenarios where the former is the clear winner. The unique properties of plastic make it an excellent material for replacing components usually made from metal.
So, what does this process involve, and how does a business follow through? More importantly, why is plastic increasing in popularity? Understanding the mechanics and the advantages of metal-to-plastic conversion is important for the future of your operations. Let’s explore the key points you need to know.
What Does Metal to Plastic Conversion Mean?
The process involves a project to convert designs you fabricate with metal and make them via plastic injection molding instead. There is a vast array of components, both large and small, that can require extensive fabrication time and unique expertise to produce in metal.
That’s not to mention the increasing expense of many metals, especially alloys with the strength for mechanical applications. Since the advent of more durable and advanced plastic resins in the mid-20th century, many manufacturers have converted metal parts into plastic components. Plastics offer a way around some of the disadvantages of metal. These drawbacks include heavyweight, fabrication difficulties, and the availability of raw materials.
If the process has been around for so long, why has a shift toward this conversion occurred only recently? To be sure, many manufacturers have already made the switch over recent decades. However, there are two factors at play. The first is the continued development of better molding technology, improved molding techniques, and the creation of more versatile and diverse resins and resin blends. The second factor is the growth of advanced tools and software to make effective part design faster and more reliable. With this option available, is it suitable to your needs?
A Quick List of Advantages of Industrial Plastics Over Metals
There are many benefits a manufacturer can unlock by making the switch to plastic. Indeed, a careful examination of the facts often reveals that plastic is a better material than metal for many applications. That fact becomes apparent when considering the eight key benefits of metal-to-plastic conversion.
Improved Efficiency Through Lower Manufacturing Costs
Metals are expensive, and there can be extensive post-manufacturing processes to consider, such as deburring. As prices for metal fabrication continue to rise, plastic resins remain widely accessible and are still more cost-effective than working solely in metal. For cost reasons alone, transitioning to plastic when possible can be a win for your business.
Faster Finishing
Completing plastic parts after molding can take place much faster than with metal. In some cases, you can skip entire steps. For example, consider a metal item that requires a process such as powder coating or paint. You can produce parts with the necessary colors and features with the right resin choices and molding methods.
Reduced Weight
It’s not difficult to imagine plastic parts being lighter than their metal counterparts. Now is the perfect time to also capitalize on reducing weight. It translates into lower product shipping costs and can contribute to a more streamlined design. Transitioning more parts to plastic could open the door to new design innovations from your engineers.
Improved Sustainability and Less Waste
Metal fabrication produces substantial waste that is challenging and expensive to recycle. On the other hand, injection molding is a decidedly efficient process that uses almost the minimum amount of plastic material. With imaginative mold designs, reducing plastic flash wastage is possible, so you pay less in material costs.
More Rapid Production Turnaround Times
One of the most significant benefits of plastic injection molding is its potential for rapid part production. Many manufacturers choose molds because they can produce an impressively high part volume in a much shorter time. Metal fabrication, even when controlled by computers and lasers, still takes longer.
Less Corrosion, More Durability
In some applications, the longevity of a well-machined metal part wins out over plastic. In many other cases, however, advanced resins offer improved durability over metal. Consider that many plastics can safely withstand high temperatures, long-term UV exposure, and even exposure to corrosive chemicals without breaking down. Plastic is better than metal when you need durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Improved Strength and Resiliency
Plastic, by definition, has a chemical structure made to stand the test of time. As with corrosion, many manufacturers have transitioned to plastic from metal because of opportunities for more robust products. From tensile strength to compressive force, well-selected resins contribute to plastic products that can deliver comparable lifetime performance to metal parts.
Broader Design Capabilities
Don’t overlook the versatility of what you can achieve in three-dimensional space with plastic. Complex metal parts are costly to design and fabricate. In contrast, plastics can achieve more versatile outcomes — especially when you factor in the potential for completing entire subassemblies in plastic.
Industries Actively Undertaking Metal to Plastic Conversions
What is plastic doing for different industrial sectors today? Conversion projects and success stories appear in many manufacturing spaces. Let’s review some areas where companies might use plastic for its advantages over metal for the same products.
- The automotive industry and the transportation sector. Especially as electric vehicles become more prevalent, many automakers have transitioned interior and exterior metal parts into plastics to reduce weight.
- Aerospace applications. Passenger-facing applications include armrests, overhead bins, window covers and more, while plastics also replace metals in flight systems.
- Lawn and garden products. Plastics offer a lightweight yet durable option to offer alternatives to some metal tools. Plastics molded with metals provide more versatile designs.
- Defense applications. Lighter weight in defense applications reduces fuel consumption and eases burdens for soldiers while providing rugged durability.
In these and other industries, plastic material choices offer robust alternatives to bulky, heavy metal solutions. The right partner can make these options accessible to your business.
Discover the Big Benefits of Relying on Advanced Plastic Materials Today
At a time when cutting costs is more critical than ever, manufacturers must strive to find ways to do so without compromising on quality or component integrity. When comparing the qualities of plastic to metal, a conversion process may be the clear choice for achieving your goals. Perfect for high volumes, specialized purposes, and use in complex assemblies, transitioning to plastic parts can be a highly effective shift for your company.
At Reliant Plastics, we have years of experience in plastic injection molding and a proven process for assisting our partners at every manufacturing stage. When your business needs to explore options for reducing reliance on expensive metals that pose persistent challenges, we can help you chart a course toward a successful metal-to-plastic conversion.